This is the first of what will be a number of posts on building out parts of a basic mission network. This network will be based on Centos 7 (Linux), with an IPA server (Linux version of Active Directory), have a local patching server, and a number of there features. Today’s article will focus entirely on the basic build of a Centos 7.0 system and will serve as the base system for all of the other lessons in the future. It is important to note that some of the configuration settings listed in the article will change in future article based on the purpose of the system (primarily disk partitions).
I will be building each of these systems as virtual machines using KVM on a Centos 7.0 system but the steps are pretty much the same when using VMWare or a bare metal system. We will make the following assumptions for this article:
- Domain Name: test.lab
- IPA Server IP Address: 192.168.1.254
- IPA Server Name: auth.test.lab
1. Select “Install Centos” from the boot screen
2. Select the desired language and click “Continue”
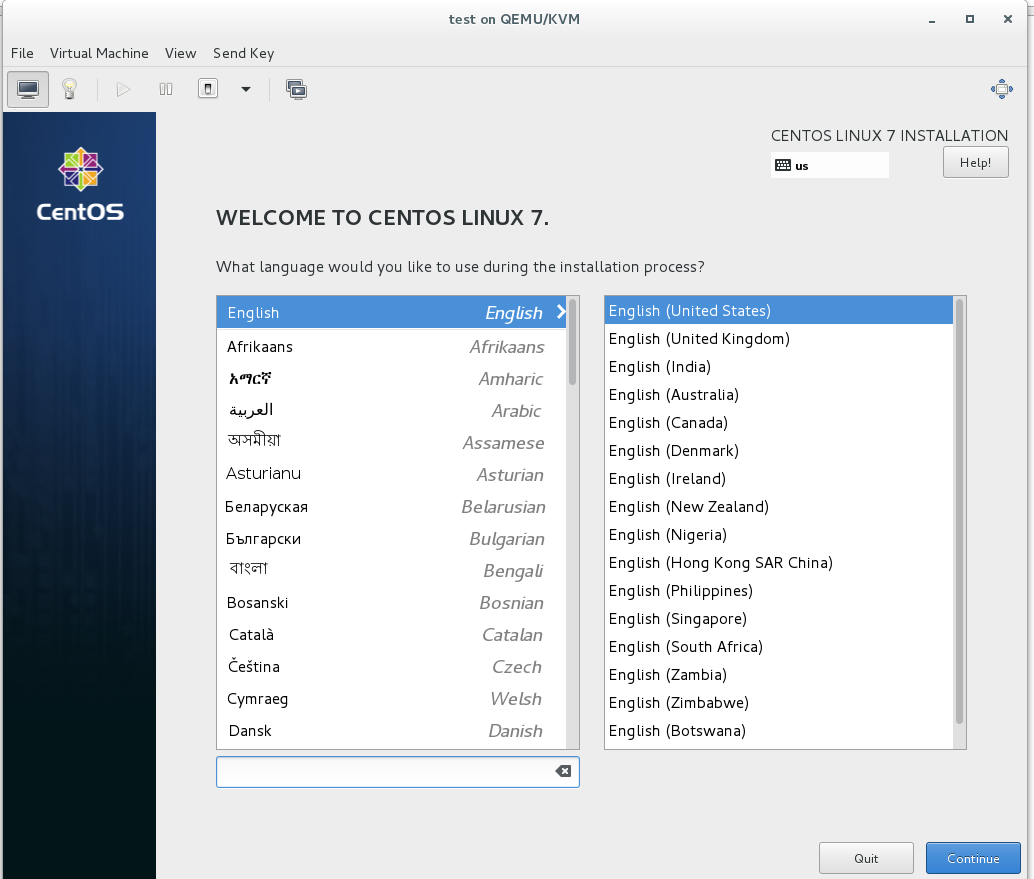
4. Configure the region to “Etc” and City to “Greenwich Mean Time”
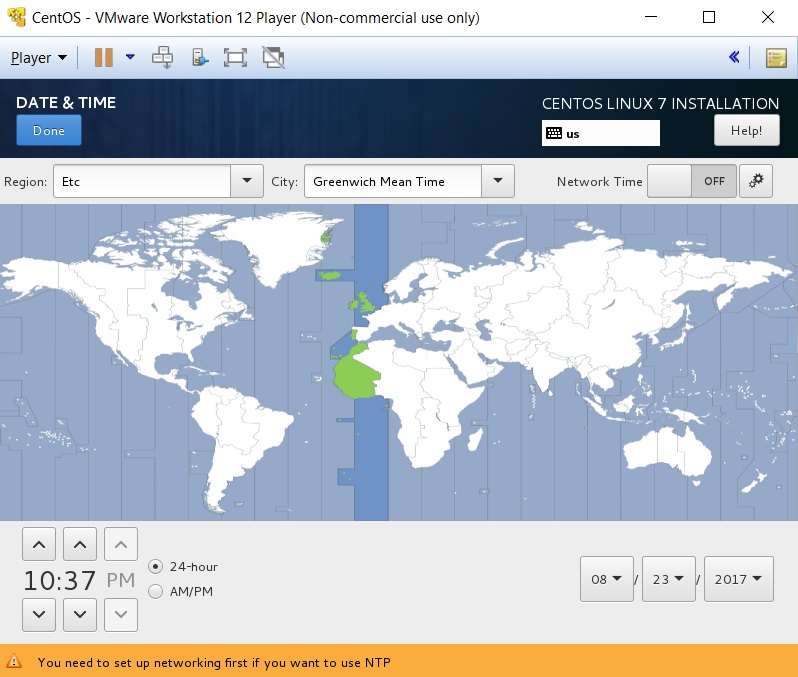
5. Select “Software Selection”
5A. Generally you will select “Infrastructure Server” but that will depend on the specific use of this system
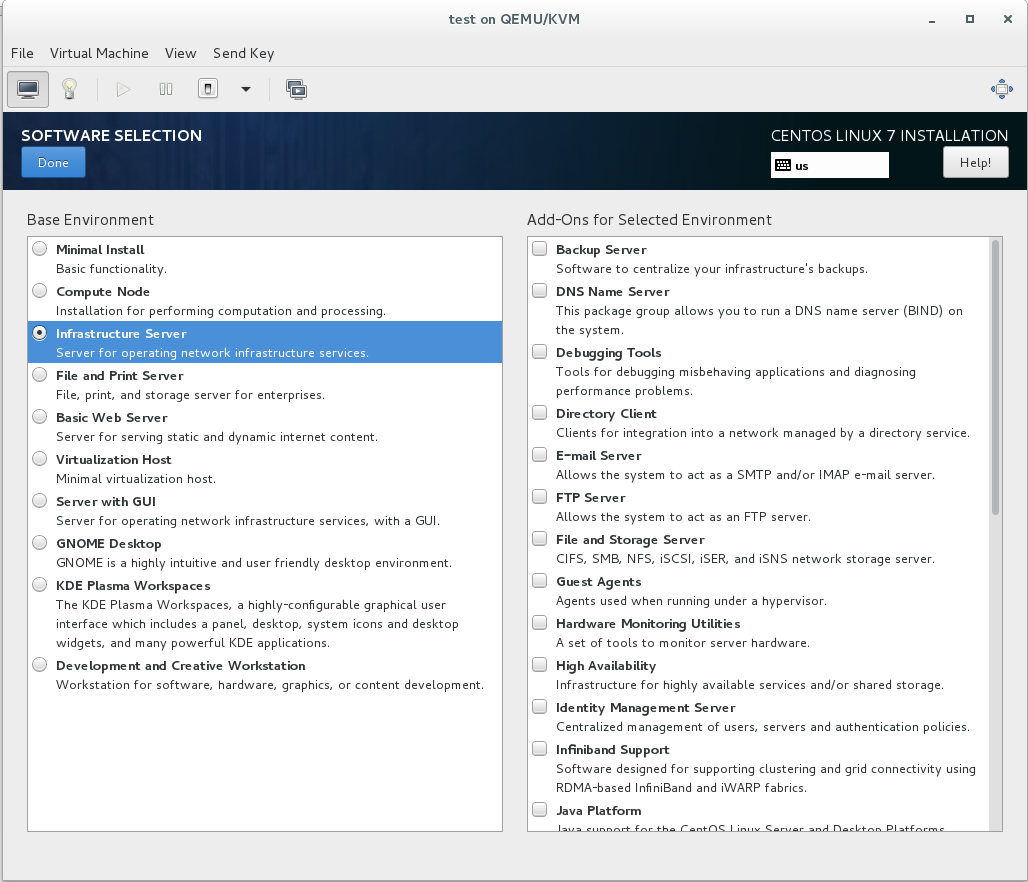
6. Select “Installation Destination”
6A. Select the radio button that says “I will configure partitioning” and select “Done”
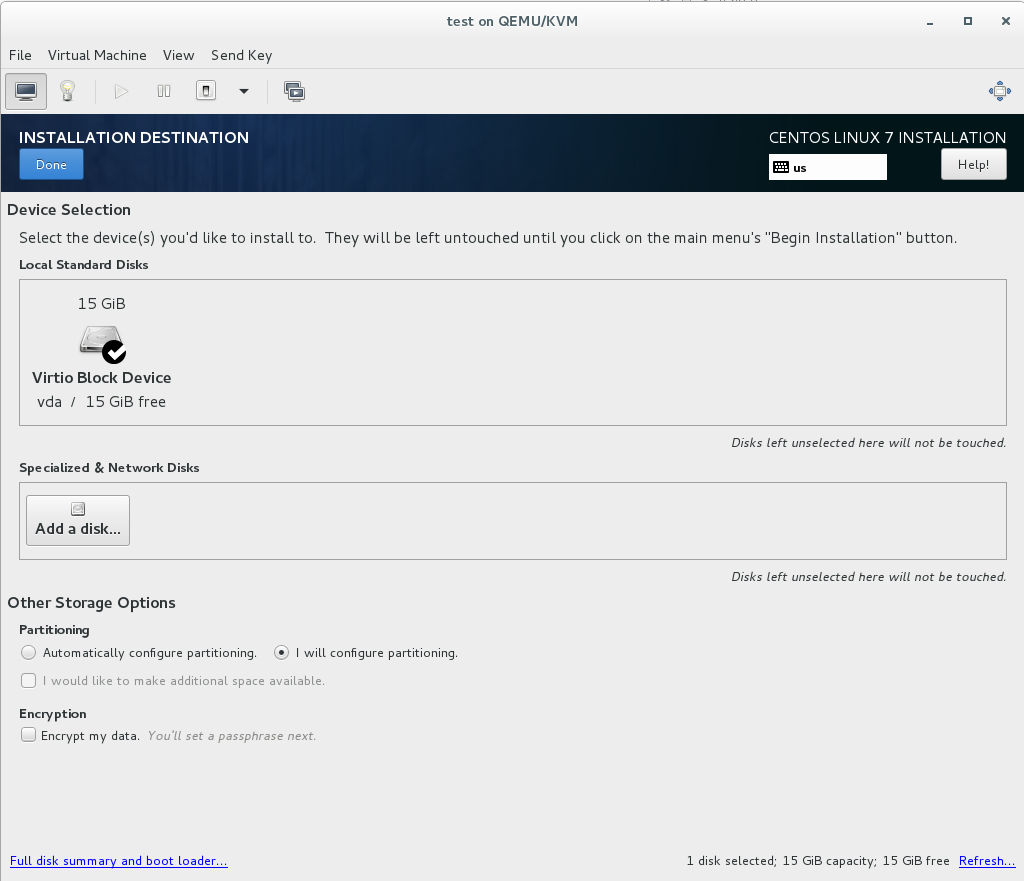
6B. Click the link to create the partitions automatically
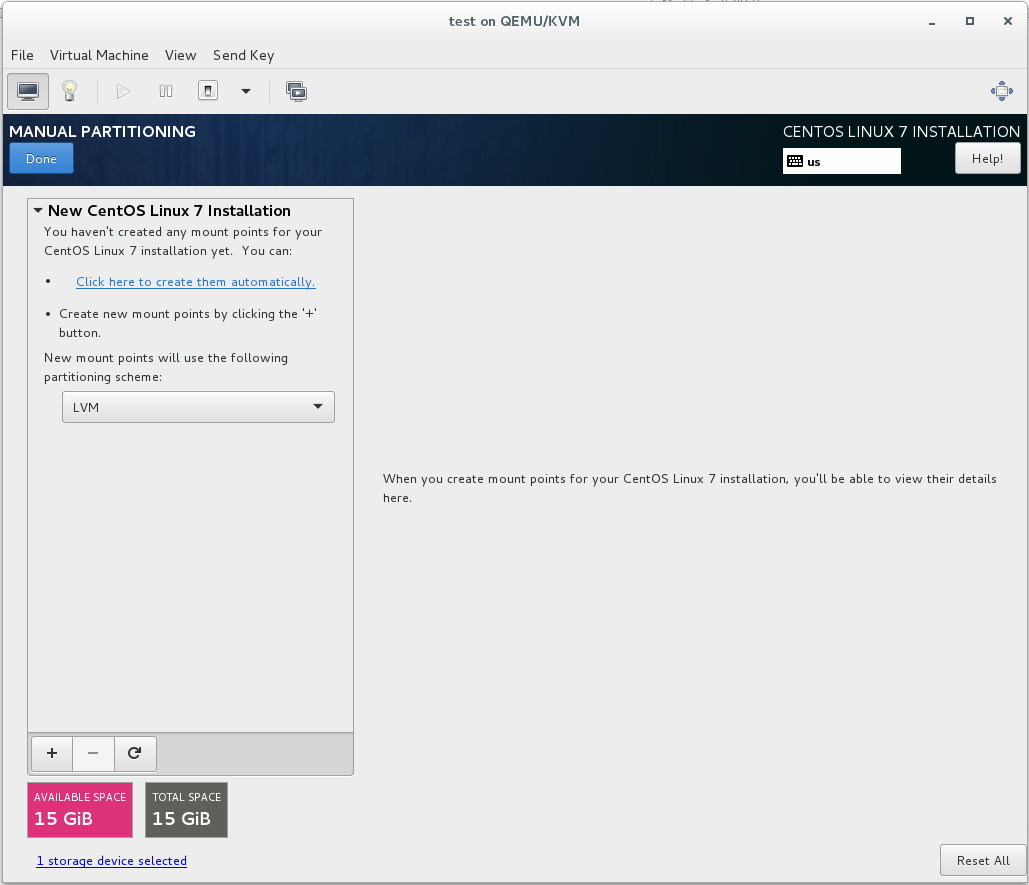
6C. When the screen updates it will have 3 partitions in it (/boot, /, and swap).
6D. Change the space in / to 2 Gib (this is just temporary) and click out of that partition to free up space
6E. Create the following partitions (Note: These are minimums. Additional partitions or more space may be required for certian uses)
- /boot 1 Gib
- Swap 2 Gib (but more may be required for some uses)
- /home 1 Gib
- /tmp 1 Gib
- /var 4 Gib
- /var/log 2 Gib
- /var/log/audit 1 Gib
6F. Select the / directory and click on “Modify” under Volume Group
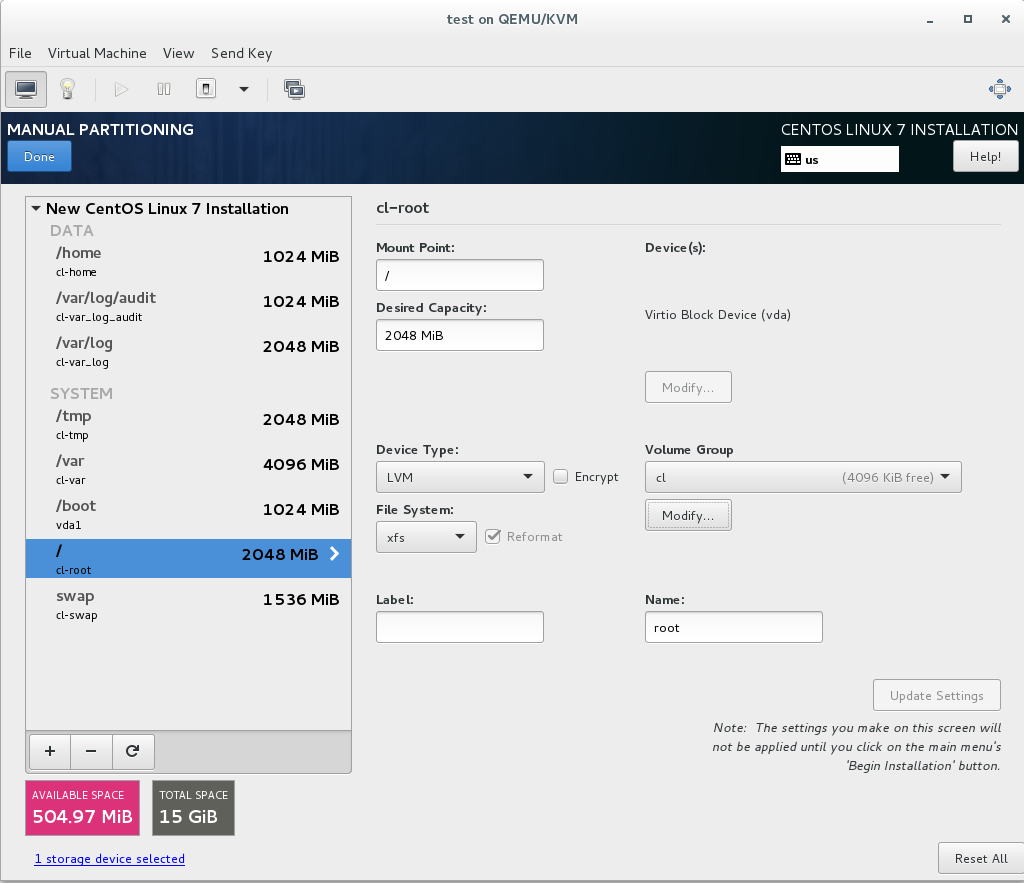
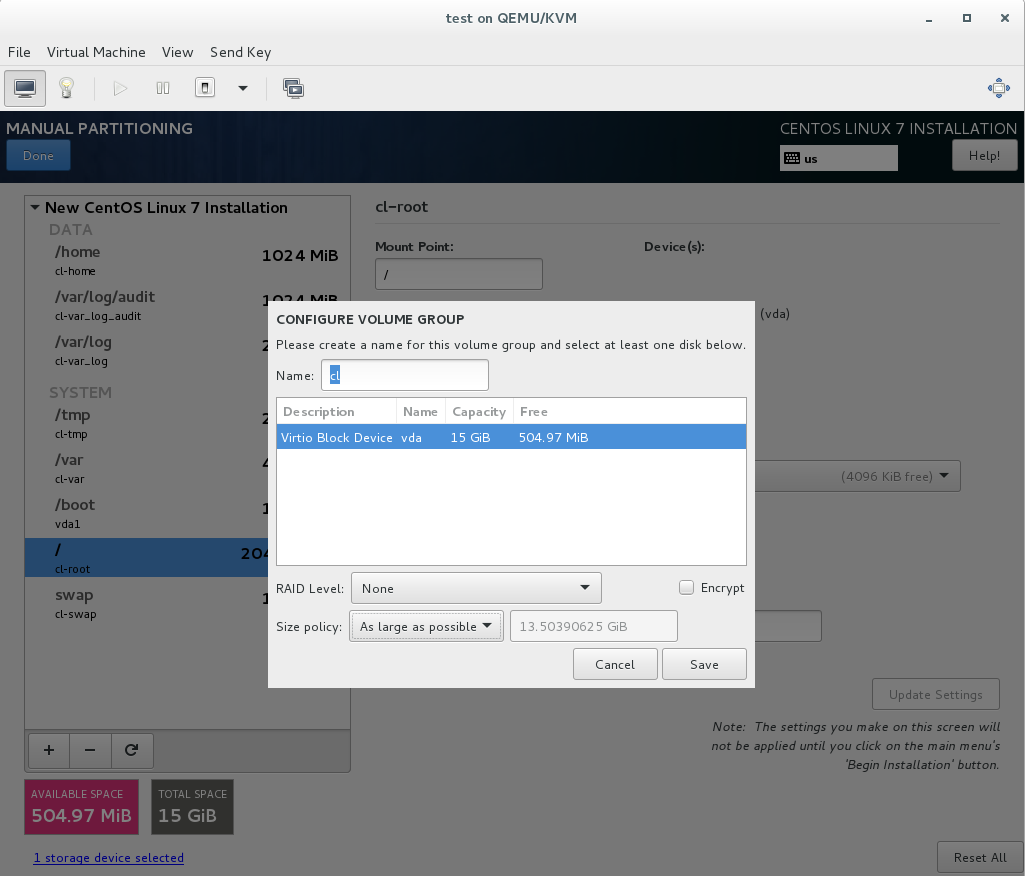
6G. Change Size Policy to “As Large as Possible” and select Save
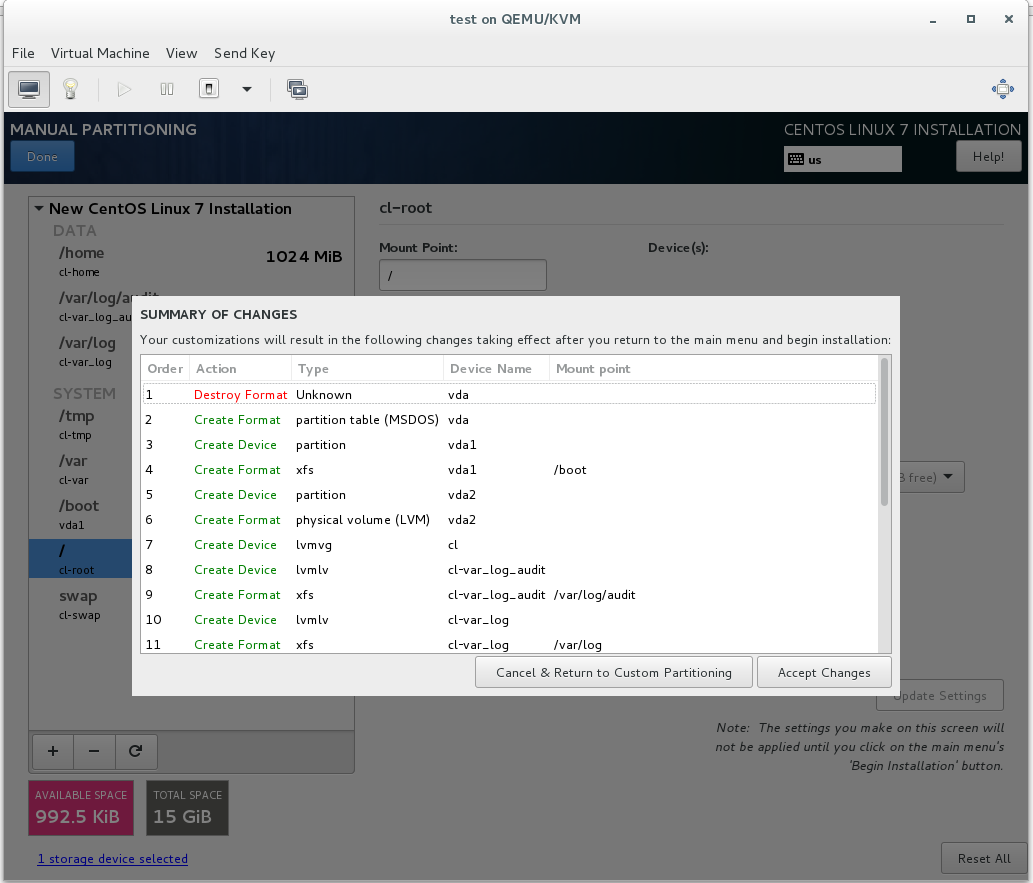
6H. Click Done and then accept the changes
7. Select “Network & Host Name”
7A. Click the “On” button next to the interface name (This will tell the system to turn on the interface on boot).
7B. Enter the computers fully qualified domain name (i.e. servername.test.lab) and click “Apply”
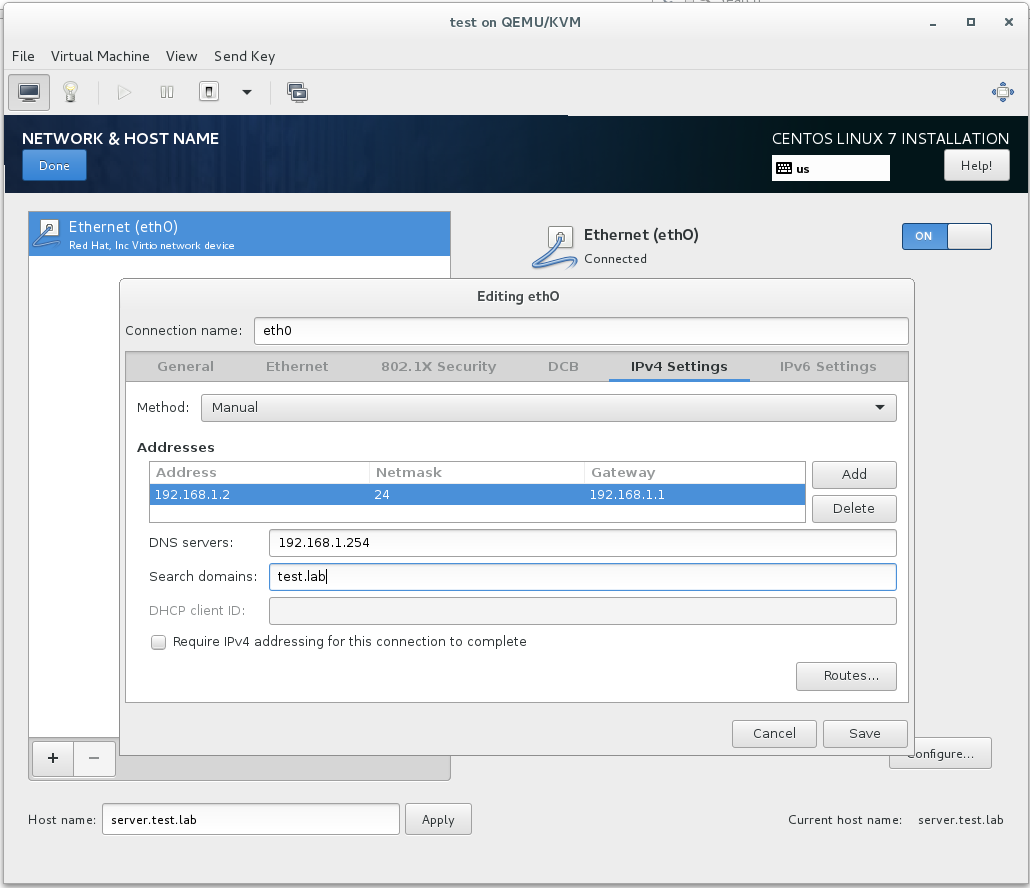
7C. Click on the “Configure” button
7D. Change “Method” to manual (static IP address)
7E. Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
7F. Enter the IP address for the IPA server under “DNS Servers”
7G. Enter test.lab under “Search Domains” and press “Save”
8. Once on the Installation Summary screen select “Begin Install”
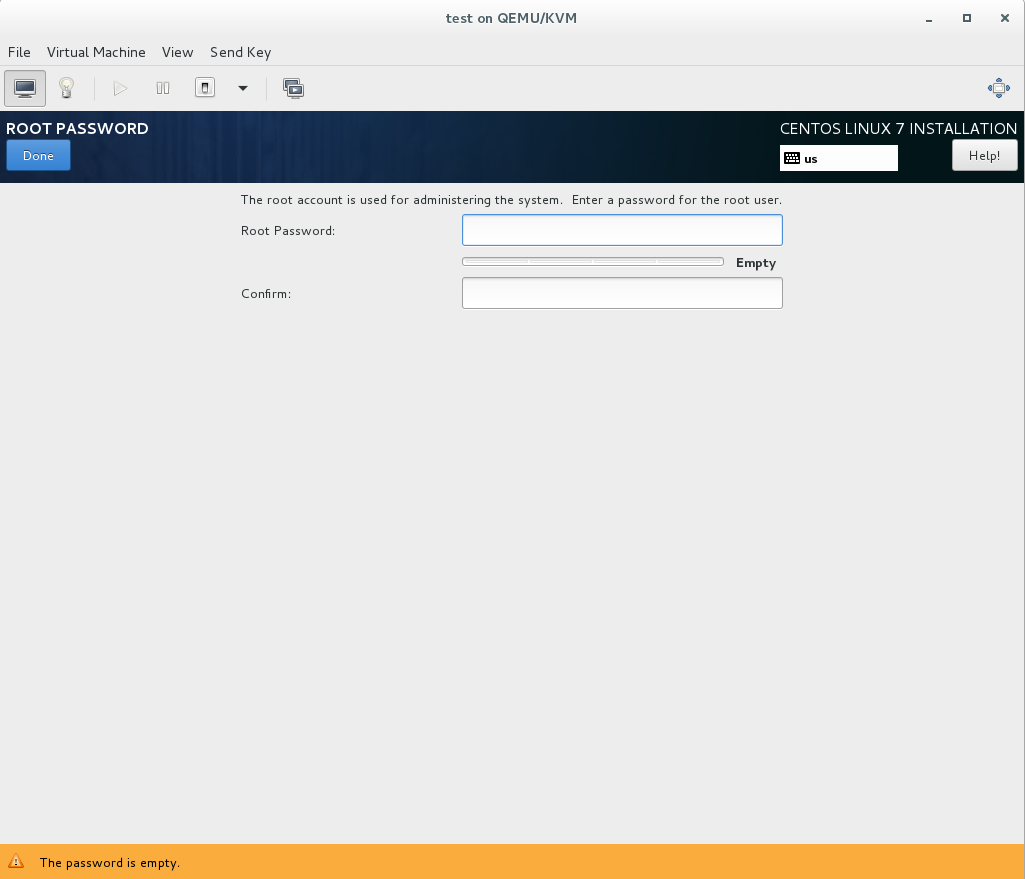
9. On the User Settings screen select “Root Password”
9A. Enter and confirm the root password and select “Done”
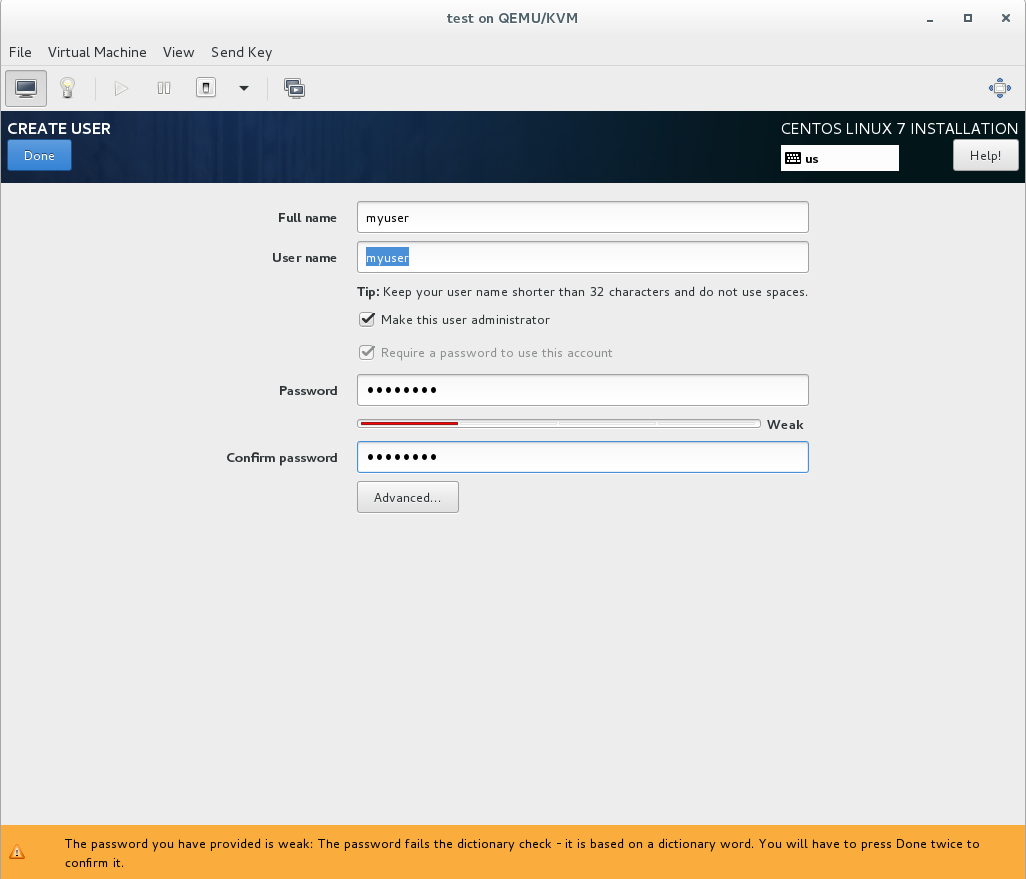
9B. Select “User Creation”
9C. Enter the username, password, and select “Make This User Administrator” and select “Done”
10. Once the installation is complete click on “Reboot”

12. Enter the command “sudo yum update -y” (Note: If you are on a closed network, you will have to update your local.repo file first)
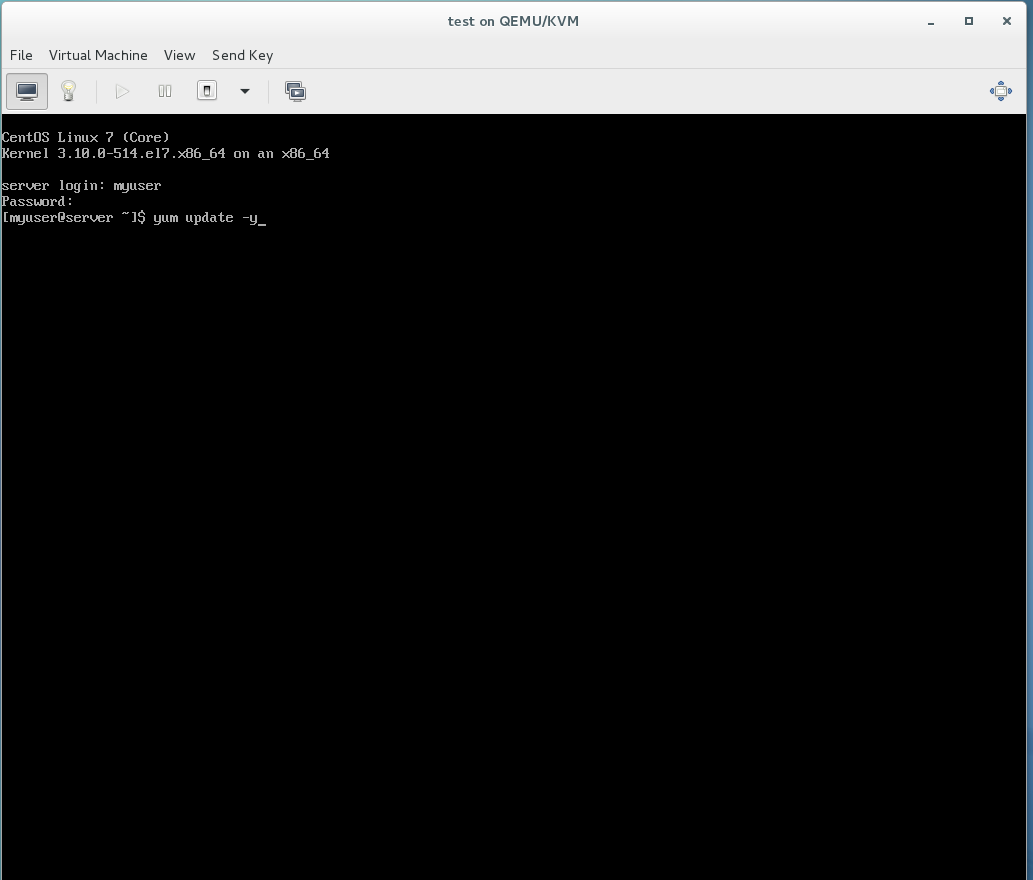
Once done reboot the system
This completes the basic system install

Will this be a STIGed CentOS build?
This initial install will not. But plan on it as a follow-up. If you choose to implement the STIG security option during the build it will take care of most of it for you automatically but I know of at least one bug in the script that will break SSHd.
I run a Centos server for SCP on my Guard domain. I think I have the STIGs right, but would like to see someone else’s build to make sure.